Money Management Tools
A page within It Make$ Cents!
What is a Budget?
A budget is an allocation and tracker for every dollar you make and spend, and it is the ultimate finance tool to help you achieve your goals. A budget is the cornerstone of personal finance. It provides a crystal-clear picture of financial health and aids in making decisions to improve financial wellbeing.
Why is a Budget Important for Financial Success?
A budget helps you achieve your aspirations by illustrating what you can and cannot afford, as well as forecasting expenses you may not see coming. It can help develop daily habits that lead to success, and help anticipate upcoming expenses. It is not uncommon to think of a budget as a tedious financial task, especially if you feel your finances are already in good order. However, it is one of the first steps to financial success and achieving your goals.
Time Based Goals
A short-term goal
A mid-term goal
A long-Term goal
Make SMART Goals
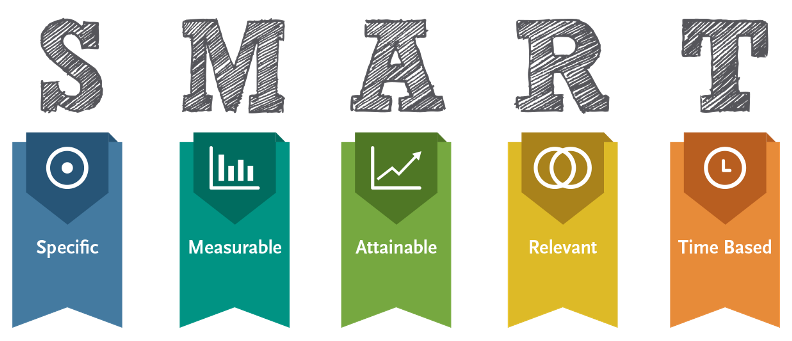 SMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time BasedSMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time Based
SMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time BasedSMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time Based
Budgeting Tips
1.) Overestimate your expenses. It is better to underestimate your income and overestimate your expenses and so that you can insure you stay on track with your budget.
2.) Underestimate your income. Working shift work can mean your paycheck will fluctuate every pay period. Salary income allows for steady hours and similar wages every pay period. Calculate your net pay with this federal paycheck calculator to determine how much your next paycheck will be to budget with.
3.) Build in an emergency fund. Emergency funds are critical to having money set aside in case of an emergency such as medical bills or a new car battery. Aim to set aside $500 or another amount that fits your needs.
4.) Set Savings Goals. Outside of maintaining a budget, setting aside money and saving is very crucial. Having some cash saved is a good idea in case you switch jobs, or you are let go. Aim to save 10% of your income per month. Some common savings goals could also include creating an emergency fund, small retirement fund, etc.
What is an Emergency Fund?
An emergency fund is a bank account with money set aside to pay for large, unexpected expenses, such as:
- unforeseen medical expenses
- home-appliance repair or replacement
- major car fixes
- unemployment
For more info, visit:
 nerdwallet logo
nerdwallet logo
https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/banking/savings/emergency-fund-why-it-matters
Savings Calculators
Budgeting Calculators
Monthly Budget (.XLSX)For Excel version, click here. |
Monthly Budget Worksheet (pdf)Budgeting Worksheet |
 IMC Budget IMC Budget |
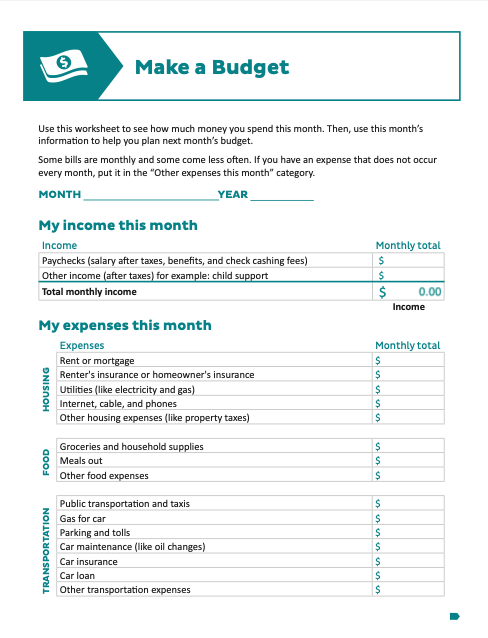 Budget Sheet IMC Budget Sheet IMC
|
Tracking Calculators
Income vs. Expense Tracker (.XLSX) |
Spending Plan Categories (.PDF) |
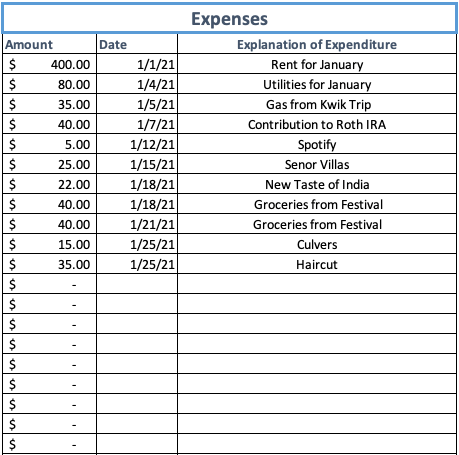 Expense vs Income CalculatorExpense vs Income Calculator Expense vs Income CalculatorExpense vs Income Calculator |
 Spending Plan CategoriesSpending Plan Categories Spending Plan CategoriesSpending Plan Categories
|
Basics of Credit Brochure
Credit Brochure
To understand the basics of credit, check out our credit-basics brochure.pdf.
 Road to Good CreditRoad to Good Credit
Road to Good CreditRoad to Good Credit
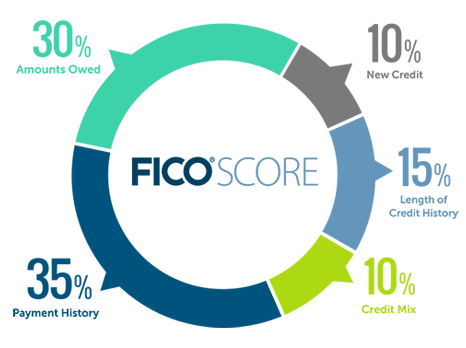
Credit Score
Credit Scores range from 300 to 850 with a higher score being better. Having a higher score will help you get approved for loans and get lower interest rates. The score reflects a person’s ability to repay debt, and it helps creditors determine if they should lend money to you.
These are the factors and their weights that determine credit scores:
Payment History: is determined by whether you pay your bills on time or not.
Amount Owed: is based on how much you are currently borrowing and how much you're allowed to borrow.
Length of Credit History: is how long you have been using credit, whether it's in the form of student loans or just using a card for small items.
New Credit: is determined by the lines of credit you have opened recently (a lot is bad).
Type of Credit: is determined by how many and the types of credit you have, including credit cards, student loans, auto loans, etc.
Credit Myths Debunked
- Credit can always be rebuilt, no matter how bad.
- Even with a bad credit score you can be approved by a lender.
- You won’t lose points for looking at your own credit score.
- A “hard pull” is when someone else pulls your credit like a potential landlord or when applying for a loan. This may lower your credit score by a few points, but will quickly return.
- Utility and cell phone payments won’t help your credit, but it may hurt if you don’t pay.
- Don’t feel a pressure to take on more debt than you can handle just to build credit. Having just one credit card will help.
Credit Reporting Agencies
There are three credit reporting agencies, credit bureaus, that collect consumer credit information and uses it to generate credit scores. Each one takes different factors into consideration which can cause you to have three different credit scores.
 Equifax Logo Equifax Logo |
 Experian Logo Experian Logo |
 transunion-logo transunion-logo |
| Equifax empowers businesses and consumers with information they can trust. With a strong heritage of innovation and leadership, we leverage our unique data, advanced analytics and proprietary technology to enrich the performance of businesses and the lives of consumers. | Experian We are the leading global information services company, providing data and analytical tools to our clients around the world. We help businesses to manage credit risk, prevent fraud, target marketing offers and automate decision-making. | TransUnion Our mission is to help people everywhere access the opportunities that lead to a higher quality of life. By helping organizations optimize their risk-based decisions and enabling consumers to understand and manage their personal information, we empower both to take their destinies into their own hands. |
Helpful Credit Sources
| Consumers can request a free copy of each of their three credit reports once every 12 months from Annual Credit Report, the only official site to access your free credit report. | |
| Credit Karma is another site where you can check your credit score for free. | |
 NerdWallet NerdWallet |
NerdWallet is a website that helps users make personal finance decisions including student loans and credit cards. |
 Fair Credit Reporting Act Fair Credit Reporting Act
|
The Federal Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) promotes the accuracy, fairness and privacy of information in the files of consumer reporting agencies. There are many types of consumer reporting agencies, including credit bureaus and specialty agencies (such as agencies that sell information about check writing histories, medical records, and rental history records). |
UW Credit Union
 UW Credit Union - La Crosse VideoUW Credit Union - La Crosse Video
UW Credit Union - La Crosse VideoUW Credit Union - La Crosse Video
- UW Credit Union works directly with the University of Wisconsin-La Crosse to offer a banking solution for students.
- Our Campus Package fits your busy lifestyle. Take care of all your banking needs quickly and easily by opening a Campus Package online or by stopping by one of our convenient campus branches.
- The Campus Package free services:
- Checking. No minimum balance.
- Free Debit Card. Unlimited ATM transactions with no fees.
- Free Online Banking. Access to balances, statements, bill pay and Money Management Tools.
- Visa® Student Credit Card. Build credit responsibly.
- Savings Account. Be prepared for future purchases or emergencies.
- Reserve Line of Credit. Your defense against bounced checks.
- Check out these additional informational videos:
 Protect ID picture
Protect ID picture
What is Identity Theft?
The Basics
Identity theft is the crime of using forged or stolen identification documents (birth certificates, social security cards, passports, etc.), usernames and passwords, or other personal information (banking pins, credit card numbers, etc.) for any purpose at all.
For more information visit these sites:
The Federal Trade Commission and Nelnet
Becoming a Victim: The Odds
(In 2019) 1-15 people had their identity stolen
1-3 US adults have experienced identity theft
Consumers lost more than $1.9 billion to identity theft and fraud in 2019
Protect Yourself
7 Signs of a scam
- The company or person does not provide their address or phone number where they can be reached.
- They require you to act immediately on the information they provide you.
- It's to good to be true.
- You're asked to move money.
- The webpage prevents you from leaving the page by using pop-ups or hijacks your browser. (close the browser and clear your history and cookies if this happens. If the browser does not close shut down the computer.)
- You receive official or professional looking mail, but the company or logo is unfamiliar.
- Search engines turn up negative results such as complaints or warnings.
5 Ways to Protect Yourself from Identity Theft
- Read your credit card and bank statements carefully and often.
- Know your payment due dates. If a bill doesn't show up when you expect it, look into it.
- Read the statements from your health insurance plan. Make sure the claims paid match the care you got.
- Shred any documents with personal and financial information.
- Review each of your three credit reports at least once a year. It's easy, and it's free. You can check your credit report here at www.annualcreditreport.com
For more tips and tools on dealing with identity theft, visit https://www.uspis.gov/tips-prevention/identity-theft or reach out to the The Federal Trade Commission.
Computer Security
If you do receive any spam messages or pushing attacks please see the link below regarding how to deal with them:
https://www.consumer.ftc.gov/articles/how-recognize-and-avoid-phishing-scams
What to do
If You Have Been Scammed
- Place a fraud alert on your credit reports and review your credit reports
- Close any accounts, including bank accounts, you know or suspect have been tampered with
- File a police report in the community where the ID theft took place
- File a complaint with the Federal Trade Commission and Wisconsin Office of Privacy Protection
- Cancel government-issued ID and obtain a replacement if appropriate
As soon as you think your information is compromised, report it to government authorities such as:
State/Local officials Consumer Action
Introduction to Investing
Investing means to expend money with the expectation of achieving a profit or material by putting it into financial plans, shares, or property, or by using to develop commercial venture.
Investment Products
Stocks
Stocks are a type of security that gives stockholders a share of ownership in a company. They are also referred to as “equities.” Investors purchase stocks mainly for capital appreciation (occurs when the stock rises in value), dividend payments (come when the company distributes some of its earning to stockholders), and ability to influence a company.
Types of Stock:
Common stock entitles owners to vote at a shareholder meeting and receive dividends. Preferred Stock owners typically do not have voting rights but do receive dividend payments before common stockholders do and have priority over common stockholders if the company goes bankrupt and its assets are liquidated.
Categories of Stock:
Growth stocks have earnings growing at an above average rate. They rarely pay dividends and investors purchase them in hope of capital appreciation.
Income stocks pay dividends consistently. They are bought for the income they generate.
Value stocks have a low price-to-earnings (PE) ratio. This means they are cheaper to buy than stocks with a higher PE ratio. Their low PE ratio may reflect that investors are not purchasing for some reason. They are purchased in the hope that the stock’s price will rebound.
Blue-chip stocks are shares in large, very well-known companies that have a favorable history of growth. They usually pay dividends, as well.
Bonds
Bonds are a debt security. Borrowers issue bonds to raise money from investors willing to lend them money for a certain amount of time. In return, the issuer promises to pay the lender a specified rate of interest during the life of the bond and to repay the principal when it comes due after a set period. Investors buy bonds because they provide a predictable stream of income, preserve capital while investing, and offset exposure to more risky stock holdings. Companies, governments, and municipalities issue bonds to receive money to finance debt, fund capital investments, and provide an operating cash flow.
Types of Bonds:
Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by private and public corporations.
Investment-grade bonds have a higher credit rating and less credit risk than high-yield bonds.
High-yield bonds have a lower credit rating and more credit risk, and therefore, offer higher interest rates in return for the increased risk.
Municipal bonds are debt securities issued by states, cities, counties and other government entities. Types of “munis” include general obligation bonds, revenue bonds, and conduit bonds.
U.S. Treasuries are issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury on behalf of the federal government. They carry full faith and credit of the U.S. government, making them a safe and popular investment. Types of U.S. Treasury debt include treasury bills, notes, bonds and Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities.
Mutual Funds
A mutual fund is a company that pools money from many investors and invests the money in securities such as stocks, bonds, and short-term debt. The combined holdings of the fund are known as its portfolio. Investors purchase shares in mutual funds and become part owners in the fund and the income it generates. Investors purchase mutual funds because they offer professional management, diversification, affordability and liquidity.
Types of Mutual Funds:
Money market funds have low risks, but they can only invest in certain high-quality, short-term investments issued by U.S. corporations, and federal, state and local governments.
Bond funds have higher risks than money market funds because they typically aim to produce higher returns.
Stock funds invest in corporate stocks. There are a variety of stock funds including growth funds, income funds, index funds and sector funds.
Target date funds hold a mixture of stocks, bonds, and other investments. They are often designed for individuals with retirement dates in mind.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
ETFs are a type of exchange-traded investment product that must register with the SEC under the 1940 Act as either open-end investment company (also known as “funds”) or a unit investment trust. ETFs are like mutual funds because they offer investors a way to pool their money in a fund that makes investment in stocks, bonds, or other assets, and in return, receive an interest in that investment pool. However, ETF shares are traded on a national stock exchange and at market prices that may or may not be the same as the net asset value of the shares.
Annuities
Annuities are a contract between you and an insurance company that requires the insurer to make payments to you, either immediately or in the future. You buy an annuity by making either a single payment or a series of payments. Your payout may come either as one lump-sum payment or as a series of payments over time. People purchase annuities to help manage their income in retirement. Annuities provide periodic payments for a certain amount of time, death benefits, and tax-deferred growth.
Types of Annuities:
Fixed Annuities are when the insurance company promises you a minimum rate of interest and a fixed amount of periodic payment.
Variable Annuities are when the insurance company allows you to direct your annuity payments to different investment options, usually mutual funds.
Indexed Annuities combine features of securities and insurance products. The insurance company credits you with a return that is based on a stock market index.
Certifications of Deposit (CDs)
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a savings account that holds a fixed amount of money for a fixed period of time.
Commodities
Commodity futures contracts are an agreement to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a specified price on a particular date in the future.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds pool money from investors and invest in securities or other types of investments with the goal of getting positive returns. Hedge funds are limited to wealthier investors who can afford the higher fees and risks of hedge fund investing, and institutional investors, including pension funds.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real estate investment trusts allow individuals to invest in large-scale, income-producing real estate. A REIT is a company that owns and operate income-producing real estate or related assets. These provide a way for individuals to earn a share of the income produced through commercial real estate ownership without buying commercial real estate.
How the Markets Work
Stock Market
Stock market is a term for the organized trading of stocks through exchanges, over-the-counter, and computerized trading venues.
Public Companies
Companies are considered public when their securities trade on public markets and when they disclose certain business and financial information regularly. A public company has public reporting obligations if they sell securities in a public offering, allow their investor base to reach a certain size, or voluntarily register with the SEC.
Market Participants
Broker-dealers charge a fee to handle trades between the buyers and sellers of securities. A broker-dealer may buy securities from their customer who is selling or sell from their own inventory to its customer who is buying.
Clearing Agencies are Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs) that are responsible for writing and enforcing their rules and disciplining members. There are two types of clearing agencies-- clearing corporations and depositories.
- Clearing corporations, such as the National Securities Clearing Corporation (NSCC) and the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation (FICC), compare member transactions, clear those trades and prepare instructions for automated settlement of those trades. Clearing corporations often act as intermediaries in making securities settlements.
- Depositories, namely The Depository Trust Company (DTC), hold securities certificates for their participants, transfer positions between participants, and maintain ownership records.
Credit Rating Agencies - Credit Rating Agencies provide opinions on the creditworthiness of a company or security. They indicate the credit quality by means of a grade. Generally, credit ratings distinguish between investment grade and non-investment grade. For example, a credit rating agency may assign a "triple A" credit rating as its top "investment grade" rating, and a "double B" credit rating or below for "non-investment grade" or "high-yield" corporate bonds. Credit rating agencies registered as such with the SEC are known as “Nationally Recognized Statistical Rating Organizations.”
Electronic Communications Networks, or ECNs, are electronic trading systems that automatically match buy and sell orders at specified prices for users of the system. ECNs register with the SEC as broker-dealers and are subject to Regulation ATS. ATSs are Alternative Trading Systems. This term includes all systems that perform securities exchange functions and are not registered with the Commission as exchanges.
Investment Advisers - Investment advisers are persons or firms that are in the business of providing investment advice to investors or issuing reports or analyses regarding securities. They do these activities for compensation.
Securities exchanges are markets where securities are bought and sold. There are 15 securities exchanges registered with the SEC as national securities exchanges, including NYSE Euronext, NASDAQ, The Chicago Board Options Exchange, and BATS Exchange. Securities Exchanges are also SROs.
Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs) manage their industry through the adoption of rules governing the conduct of its members. SROs also enforce the rules they adopt and discipline members for violating SRO rules. Two well-known SROs are the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (MSRB). FINRA is the largest SRO in the securities industry. It is the frontline regulator of broker-dealers. MSRB makes rules regulating dealers of municipal securities. The SEC oversees both FINRA and the MSRB. Other SROs include clearing agencies and securities exchanges.
Transfer agents record changes of security ownership, maintain the issuer's security holder records, cancel and issue certificates, and distribute dividends. Transfer agents stand between issuing companies and security holders. The purpose is to facilitate the punctual and accurate clearance and settlement of securities transactions and assure the safeguarding of securities and funds.
Types of Orders
A market order is an order to buy or sell a security immediately. This type of order guarantees that the order will be executed but does not guarantee the execution price. A market order generally will execute at or near the current bid (for a sell order) or ask (for a buy order) price.
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. A buy limit order can only be executed at the limit price or lower, and a sell limit order can only be executed at the limit price or higher.
A stop order, also known as a stop-loss order, is an order to buy or sell a stock once the price of the stock reaches the specified price, known as the stop price. When the stop price is reached, a stop order becomes a market order.
A buy stop order is entered at a stop price above the current market price. Investors generally use a buy stop order to limit a loss or protect a profit on a stock that they have sold short. A sell stop order is entered at a stop price below the current market price. Investors generally use a sell stop order to limit a loss or protect a profit on a stock they own.
Types of Brokerage Accounts
A cash account is a type of brokerage account in which the investor must pay the full amount for securities purchased. In a cash account, you are not allowed to borrow funds from your broker to pay for transactions in the account.
A margin account is a type of brokerage account in which your brokerage firm can lend you money to buy securities, with the securities in your portfolio serving as collateral for the loan. As with any other loan, you will incur interest costs when you buy securities on margin.
Stock Purchases and Sales: Long and Short
A long position in a security means that you own that security with the expectation that the stock will rise in value.
A short position is the sale of a stock you do not own. Investors who sell short think the price of the stock will decrease in value in the future. If the price does decrease, you can buy the stock at the lower price and make a profit. If the stock increases in value and you buy it back later, you will have a loss.
IMC! Investing Tools
Investing Basics (.PDF) |
Investing Brochure (.PDF) |
 investing basics investing basics |
 investing brochure investing brochure |
Investing Game Plan
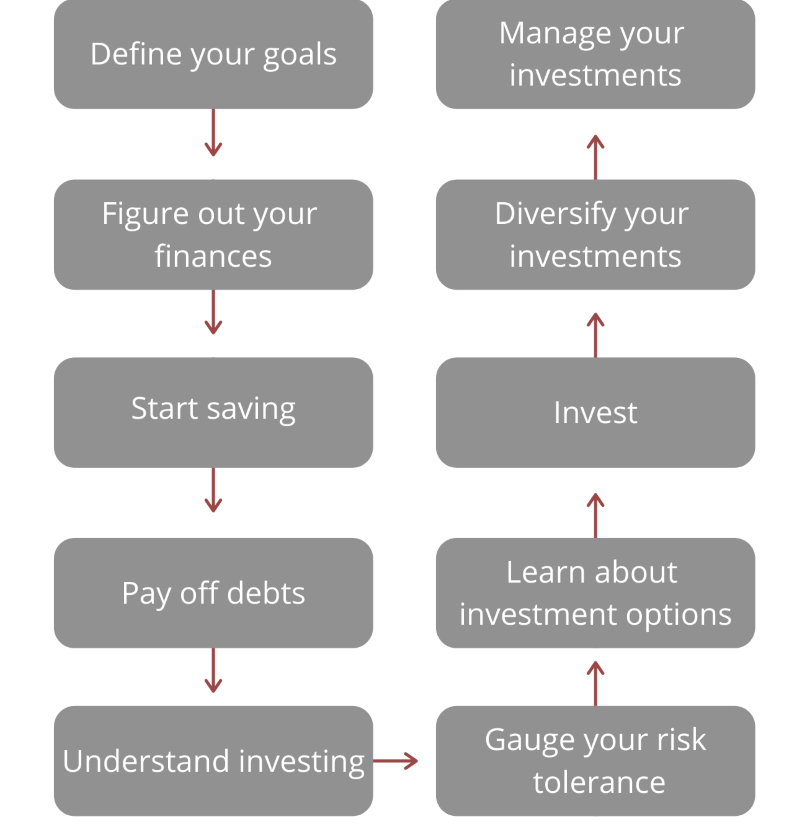 investing chart
investing chart
Retirement and Retirement Plans
Retirement
A retirement savings plan is a critical part of securing your retirement. There are many investment options to improve your retirement. For more information, please visit Employment to Retirement.
Financial Tools and Calculators
 Job Search
Job Search
Finding a job can be a daunting task, especially after graduating college. It can feel like there are so many hoops and hurdles that it becomes overwhelming. To help you navigate through this process, we have outlined a path to get you started on finding the next step of your career.
If you would like a personalized meeting, you can schedule an appointment with IMC or Career Services; we are happy to give you advice, but Career Services will have the expertise on this subject.
Job blocks
Preparation
Putting in a little work upfront will be the ultimate time saver in this process. Before applying to specific positions, it is important to have relevant documents updated. This is also the time to put thought towards where you want to live. This will affect your cost of living, job demand, and consequentially net income. Keep in mind these documents may need special attention to include information specific to your field.
Academic Transcripts – Your transcripts are not usually a piece of the overall application, but it contains useful information for building a resume (relevant coursework, GPA, etc.).
Resumé – No one has a perfect resumé, but there are key elements you must include to have a competitive resume. Here is a guide to writing a resume. It would be good to go through especially if it has been a while since looking at your resume.
Cover Letter – Cover letters are your chance to showcase your personality and dive deeper on your selling points. The substance of a cover letter can vary significantly depending on your industry. Here are some tips everyone can implement when writing an effective cover letter.
Clean Your Web - It has become common practice for employers to search for your profile on social networking sites. Make sure all of your social media posts are appropriate and your photos don't portray you as an unstable worker.
Searching
Job Fairs
Job fairs are a great place to mingle with potential employers and get a feel for companies. UWL hosts several job fairs throughout the year. Visit the Career Services page and look under the events column for a look into all of our fairs and workshops. Remember to bring several copies of your resumé!
Search engines
Sometimes a keyword search such as "editing jobs" or "accounting positions" is all you need to turn up potential employers. UWL has partnered with Handshake, a great resource to help connect you with potential employers. Another popular website tailored to find you a job is Indeed, but don't just look at one and hope for the best. You should be open and look everywhere you can until you find and land that perfect job!
Knowing someone on the inside
Having a friend who works somewhere you would like to work gives you an edge on getting that job. If your friend is a good employee and refers you to their boss, there's a better chance you'll get the job based on their recommendation.
Search the Area
If you know where you want to work, another option would be to search for companies in that area and apply through their website. Not all employers will post their jobs on a search engine, so doing a more focused search of regional areas is a way to find jobs that are not broadcasted nationwide.
Interview
Be Prepared
Research the organization you're applying for. Know what the average salary and federal salary paycheck is for this position you are interviewing for and how your experience and education measure up. Visit their website, read their mission statement, and read articles about them so that if you're asked questions about the company you have some ready-to-go answers.
Come with questions. Look up common interview questions and have pre-thought-out responses. Be honest if you need a moment to think through a question. Be prepared to answer questions about your previous employers, your coworkers, your hobbies, etc. Also, try checking out Career Service’s Interviewing Basics.
Be Professional
 Job Search ApparelEmployers want to know they are hiring a professional, and dressing the part is important to that end. A good rule of thumb is to dress a notch above what the job's dress code requires. For example, if the job requires a collared shirt and tie, wear a suit. If the job only requires a company t-shirt, wear a collared shirt to the interview. If the job requires a suit, wear your best suit.
Job Search ApparelEmployers want to know they are hiring a professional, and dressing the part is important to that end. A good rule of thumb is to dress a notch above what the job's dress code requires. For example, if the job requires a collared shirt and tie, wear a suit. If the job only requires a company t-shirt, wear a collared shirt to the interview. If the job requires a suit, wear your best suit.
Even if you look nice, employers are also looking for good people skills. Introducing yourself, shaking hands, remembering please and thank you, eye contact, and smiling are the key to successful interview.
Be Relaxed
It sounds simple enough, but anyone who has been in a job interview knows this is one of the most difficult parts. Being relaxed helps portray your confidence that you are able to do your job effectively and gives the interviewers a sense of your individual personality. Check out this list of ways to calm the nerves before an interview to help you be at your best during this important step.
Post Interview
The Follow-up
After your interview, be sure to ask for your interviewer's contact information so you can send them a thank you email. Sending a follow-up email within a few days of an interview will set you apart from the crowd. Keep it short, include anything important that you forgot to mention during the interview, and thank them for the opportunity. This is a two-parter though. Statistics show that a second follow-up email will also improve your chances of getting hired. Send the second email to the hiring manager asking about the status of your application two to four weeks after the interview. In the email also include the position, date, and place of the interview. Also, bring up a specific topic that you talked about during your interview to express your interest in the position. Again, keep it short and polite.
Making the Best Decision
Were you offered more than one job? View our brochure to make the best decision. Two Job Offers?
Different locations? Get a good idea the cost of living from the different cities/states. This will make a big difference in how far your salary will stretch.
It is important to know how to negotiate a job offer too. Your starting salary will make big difference in the long run.
Health Insurance for those Under the Age of 26
If your parent’s health insurance plan covers dependents, you usually can be added to their plan and stay on it until you turn 26. This is true even for those who: Get married, have or adopt a child, start or leave school, live with our without your parents, are or are not claimed as a tax dependent, or turn down your employers health insurance.
 Health Insurance
Health Insurance
Health Insurance for those not on their Parent's Insurance
BadgerCare
- BadgerCare Plus is a health care coverage program for low-income Wisconsin residents.
- Click to see BadgerCare fact sheet for more information: https://www.dhs.wisconsin.gov/publications/p1/p10179.pdf
 BadgerCare
BadgerCare
Other Options
- Check out this list of highly rated providers for college students: https://www.investopedia.com/best-health-insurance-for-college-students-5086827
Options with No Health Insurance
Student Health Center
- The Student Health Center provides a wide range of low cost services to students of UWL and WTC both in person and virtually. Undergraduate or graduate students currently enrolled with ≥1 credits do NOT pay SHC user fees but services specific fees may apply.
 Student Health Center
Student Health Center
- To learn more about the student health center, services, hours of operations, and fees please click here or visit the SHC at 1300 Bager Street.
La Crosse Neighborhood Family Clinics
- The La Crosse Neighborhood Family Clinic that is an affordable and accessible alternative to most Doctor's Offices with offices in La Crosse, Onalaska, Sparta, and Viroqua. Patients do not need to worry about insurance and complicated forms but rather pay at the time of service with transparent and upfront pricing.
- Visit http://mynfclinics.com to learn more
Car Insurance
It is important to have proper car insurance in the event of an accident. In the state of Wisconsin, it is required drivers have liability insurance at the minimum. Below are two great resources for shopping for car insurance.
- https://www.moneyunder30.com/best-car-insurance-for-college-students
- https://secure.money.com/car-insurance/lp/compare-car-insurance?utm_campaign=car-ins-comparison-tool&utm_source=newsletter-special-send&utm_medium=email&xid=sendgrid
 Car Insurance
Car Insurance
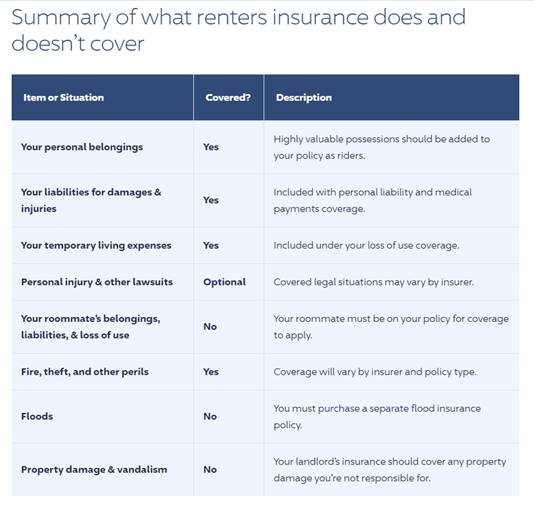
Renters Insurance
Do I need renters insurance?
- Renters insurance isn’t legally required, though certain apartment complexes and landlords may require it. As a result, only 37% of renters carry a renters policy, according to III.org. But regardless of whether it’s required, it’s always a good idea to get renters insurance to cover your stuff.
How much does a typical renters insurance policy cost per month?
- The average cost of renters insurance in the US is about $14.90 per month, according to data from the Insurance Information Institute. The average renter can expect to pay about $179 per year in total for coverage https://www.businessinsider.com/personal-finance/average-cost-renters-insurance