Medical Emergency
A page within University Police Department
What to Do in a Medical Emergency
In the event of an injury or illness that appears to be an emergency, take the following steps:
Immediate Emergency Actions
- Call 911 for serious injuries or life-threatening conditions. Provide the location, describe the situation, and explain the victim's condition. Do not hang up until the dispatcher tells you to do so.
- Provide first aid within the scope of your abilities and training.
- Wait for emergency personnel to arrive and assume care. Share any relevant information with them.
- Do not move the injured or ill person unless there is an immediate threat to their life. Keep them as comfortable as possible until help arrives.
- Do not administer medications unless they are the individual's own, and only with their verbal permission.
- Be aware that certain behaviors may resemble intoxication but could be the result of a medical condition.
Identifying Specific Medical Emergencies
Head trauma
Caused by an impact to the head or face. Do not move the person unless absolutely necessary. Wait for first responders.
Signs may include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Worsening headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Uneven or dilated pupils
- Clear fluid from the nose or ears
- Confusion or slurred speech
Bleeding
Bleeding severity depends on the source of the injury.
- Capillary bleeding: Minor surface bleeding, often from abrasions. Clean the wound and cover it if bleeding slows on its own.
- Venous bleeding: Steady flow from a vein. Apply direct pressure with a clean bandage. If bleeding continues or the wound appears deep, seek medical attention.
- Arterial bleeding: Spurting blood from a deep wound. This is life-threatening. Call 911 and apply firm pressure immediately.
- Stop the Bleed kits are stored inside all AED cabinets.
Seizure
A sudden electrical disturbance in the brain. Protect the individual by clearing the area of objects that could cause injury.
Common symptoms:
- Sudden collapse
- Loss of consciousness
- Jerking or uncontrollable muscle movements
- Clenched jaw or teeth
- Rapid eye movement
Heart attack
A disruption in normal heart function that can be fatal if untreated.
Warning signs:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Pressure in the neck, back, or arms
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or stomach pain
- Fatigue or dizziness
Note: Women may experience more subtle or different symptoms than men. - AED's are located in numerous locations throughout the University.
Stroke
Caused by a blockage or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain. Quick response is critical.
Use the FAST checklist:
- Facial drooping: Ask them to smile. One side of the face may sag.
- Arm weakness: Ask them to raise both arms. One may drift downward.
- Speech difficulties: Look for slurred or confused speech.
- Time: Call 911 immediately. Rapid treatment is essential.
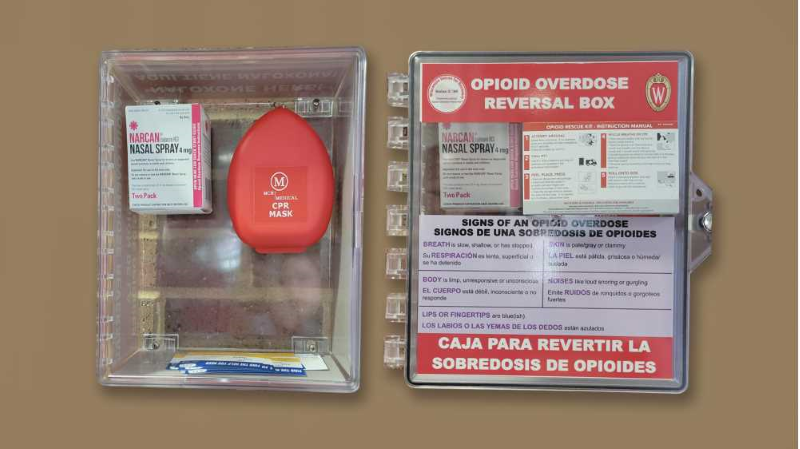
Alcohol poisoning or drug overdose
Potentially fatal result of consuming too much alcohol or drugs.
Signs include:
- Vomiting or unresponsiveness
- Loss of consciousness
- Irregular, shallow, or slow breathing
- Unusual skin color, either very pale or flushed
- Nalox-Zone boxes have been installed in all 10 residence halls